» Thomson electrometer modified by Lang (0352)
Immagini



DESCRIPTION
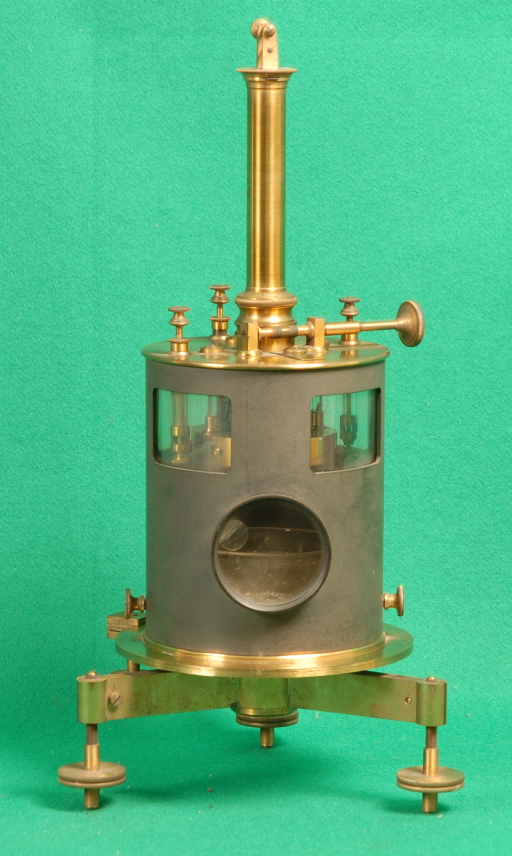
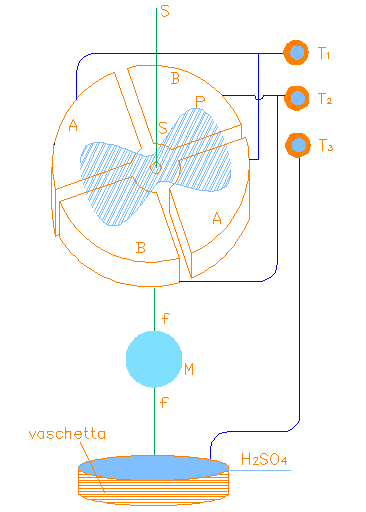
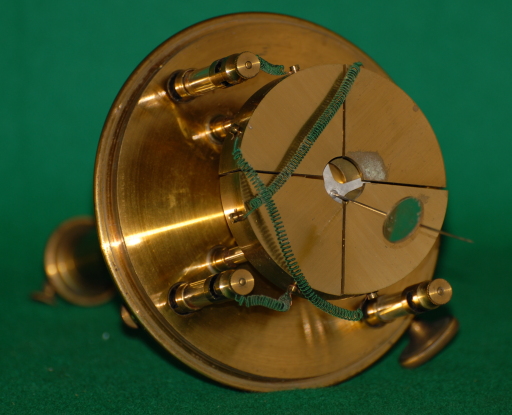
Exhibit 352 is a Thomson electrometer as modified by Lang. It is composed of four empty cylindrical quadrants in which an 8-shaped wing can rotate according to the electric fields and the torsion in its platinum support SS. The instrument is enclosed in a brass cylinder which can rotate on its brass base with three screws (for leveling) to a position fixed with another screw. The base has a connection to ground. Each quadrant is visible through its own window in the external brass cylinder and a mirror M mounted on the platinum support is visible through its window. The opposite quadrants AA and BB are connected together and connected to the external terminals T1 and T2 (see design 1 and 2). There is a wire ff attached to Exhibit 352 is a Thomson electrometer as modified by Lang. It is composed othe lower part of the wing which besides carrying the mirror extends into a container of sulfuric acid which establishes the electrical contact between the wing and the external source of voltage at terminal T3. The mirror attached to the wire ff reflects a ray of light to a graduated scale in order to obtain an amplification of the torsional rotation. The reading is effected according to the Poggendorff method as illustrated in exhibit 287.
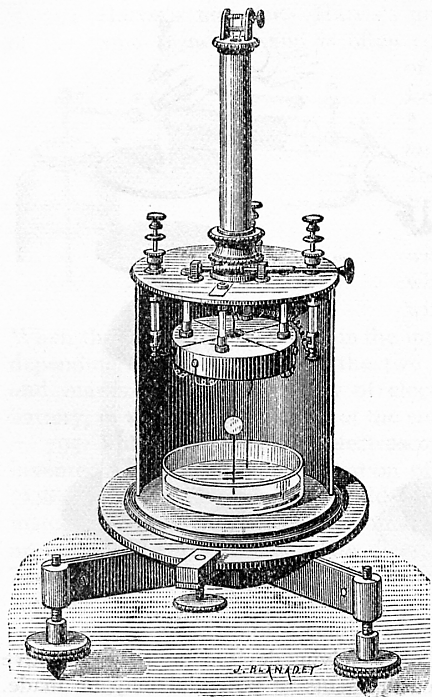
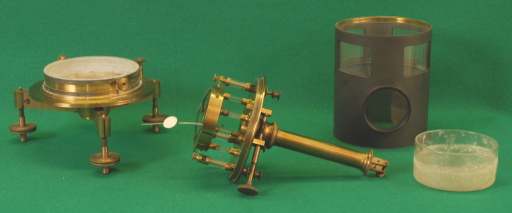
Photo 1 visualizes the mounted instrument; photo 2 shows (from left to right) the four principal parts: the base with the leveling screws, the quadrant section, the external cylinder with the windows and the container of sulfuric acid.
The instrument can be employed in different ways (see ref [1], page 370): If the unknown potential of the wing is very large respect to that of the quadrants, then the rotation of the wing is given by EQ01: [ \alpha = K(V_2 - V_1)V_p ]. where K Poggendorff is a constant that one determines by calibrating with known potentials α is the angle of rotation of the wing V1 and V2 are the potential of the quadrants AA e BB, respectively If the wing is connected to a couple of quadrants, for example BB, one has : Vp = V2 EQ02: [ \alpha = \frac{K}{2}(V_p-V_1)^2 ]. Then the deviation is proportional to the square of the difference of potential of the wing and the quadrant AA. This method is used for the measurement of potential in the case of alternating current. A simple method is to connect the two quadrant couples to equal but opposite potentials, that is V1 = - V2; Then one has EQ03: [ \alpha = 2KV_1 V_p ]. and the deviation is proportional to the potential Vp of the wing.
ISCRIZIONI
Inciso sulla base di ottone: J. Carpentier, Paris, 3429 - 25
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- [1] Oreste Murani, Trattato Elementare di Fisica, Vol. II, ULRICO HOEPLI, Milano, 1906. §238, Pag. 369.
- [2] Atkinson and Reinold, Ganot's Physics, Longmans, Green, and Co. London and Bombay, 1902. §796, Pag. 797
- [3] Worsnop and Flint, Advanced Practical Physics for Students, Chapter XXIII, pag. 643.
- [4] P. Fleury, J.P. Mathieu, Correnti variabili, Onde elettromagnetiche, Zanichelli, Bologna, 1965. §11.7, Pag. 314.
Dati Catalografici
| Data di costruzione: | --- |
|---|---|
| Data di carico: | 1885-02-10 |
| Nr. Inventario: | Cons 82 (Consorzio Univ. di Torino) |
| Costruttore: | J. Carpentier |
| Materiale: | ottone, vetro, metallo |
| Dimensioni: | Lato base triangolare: 19 cm; Altezza complessiva: 37 cm Diametro cilindro di ottone: 12 cm; altezza cilindro: 14 cm |
| Conservazione: | buono (Il filo di sospensione (ss) è rotto e manca l'acido solforico.) |
